Liver And Heart Disease
Liver and heart disease. The following are key points to remember from this review on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the heart. These ascites are mostly associated with liver cirrhosis but in fact it can also be a symptom of heart failure. A patient with a lot of liver dysfunction often develops cardiac disease.
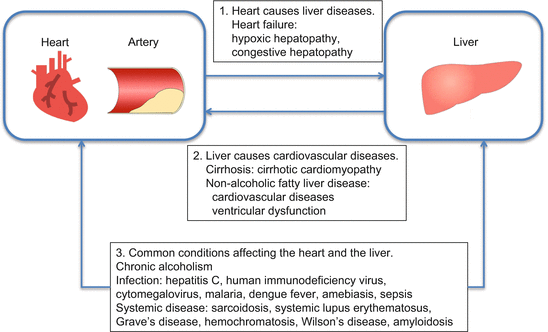
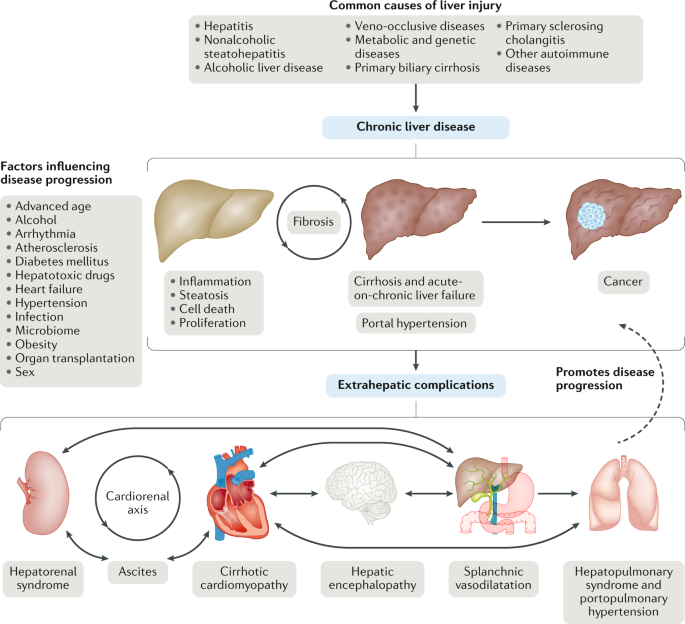
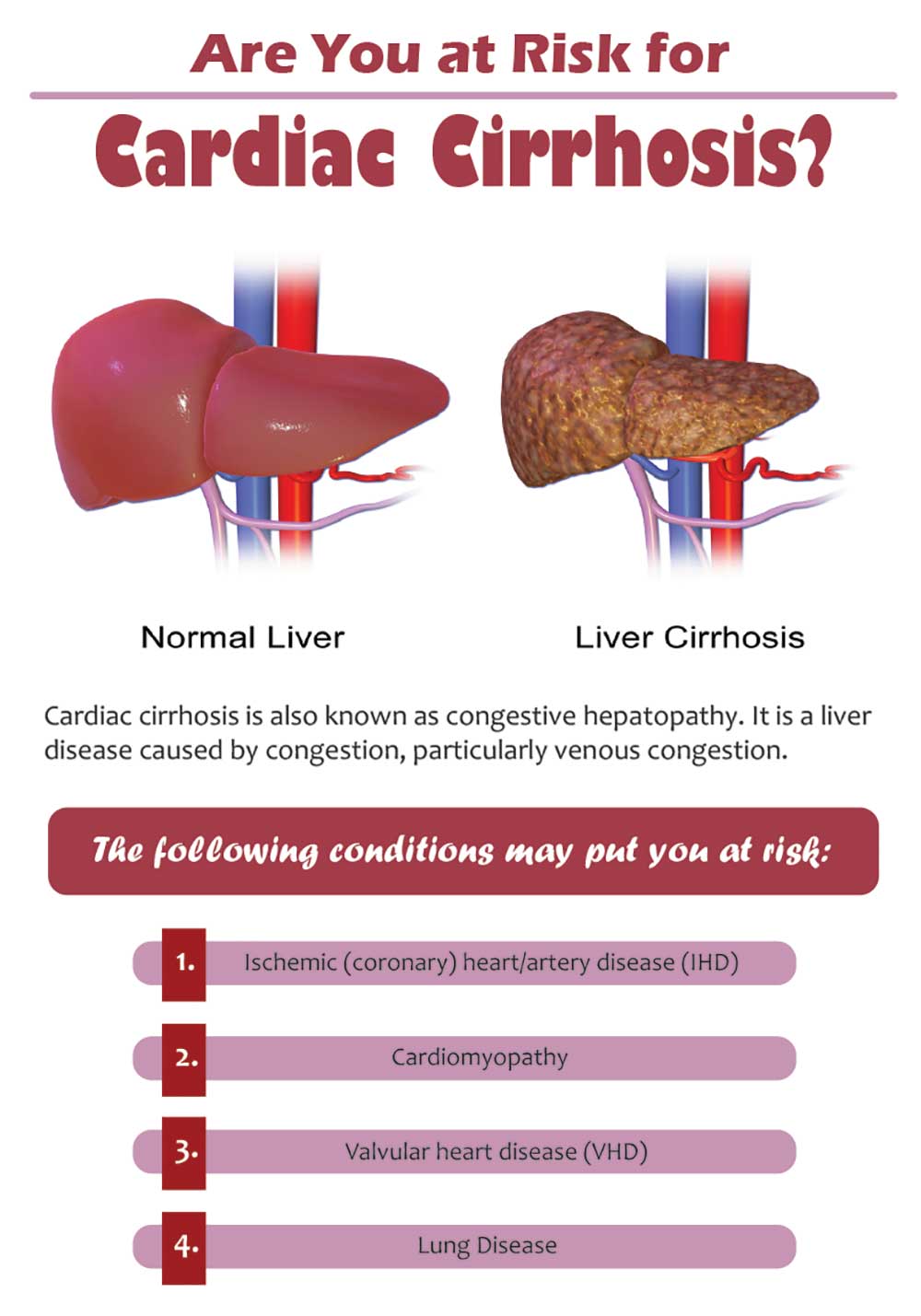
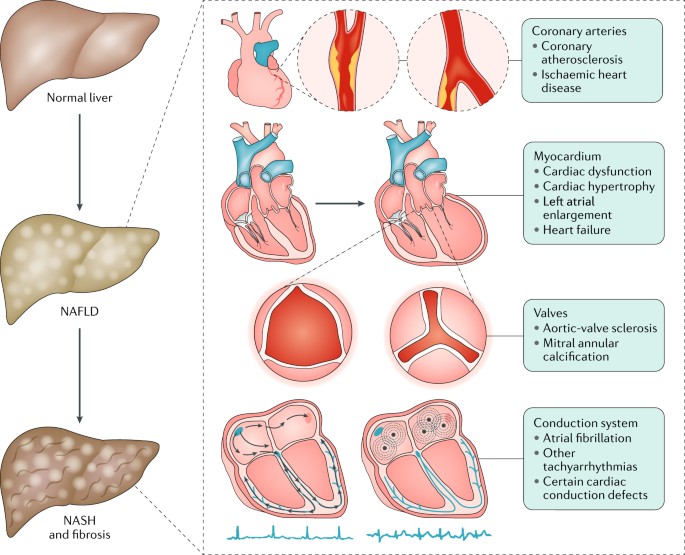
This review provides new data demonstrating the relationship between cardiometabolic risk factors coronary heart and other cardiovascular diseases and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The liver diseases affecting the heart include complications of cirrhosis such as hepatopulmonary syndrome portopulmonary hypertension pericardial effusion and cirrhotic cardiomyopathy as well as noncirrhotic cardiac disorders such as high-output failure caused by. Thus it appears that hepatic congestion secondary to right-sided heart disease may prime the liver for ischemic insults from low cardiac output and reduced hepatic blood flow and oxygenation due to left-sided heart failure.
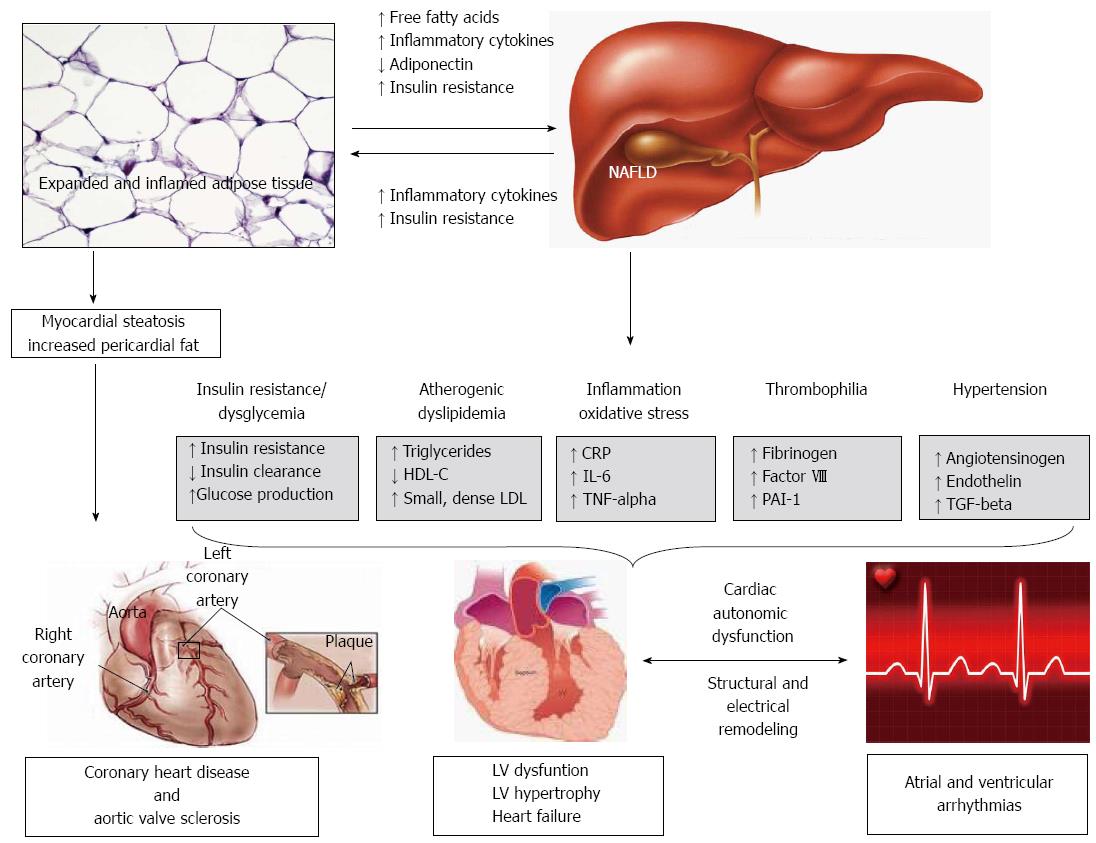
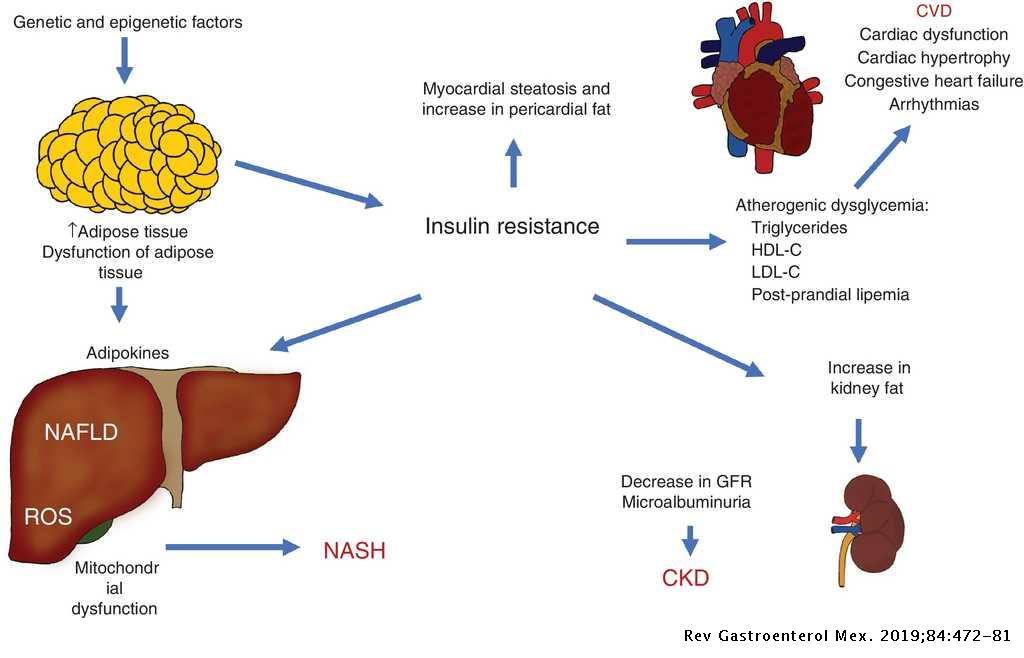
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD is being increasingly recognized as the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. It converts food into fuel processes cholesterol clears harmful toxins from the blood and makes proteins that help. Heart failure HF and liver disease often co-exist because of systemic disorders and diseases that affect both organs alcohol abuse drugs inflammation autoimmunity infections as well as because of complex cardiohepatic interactions.
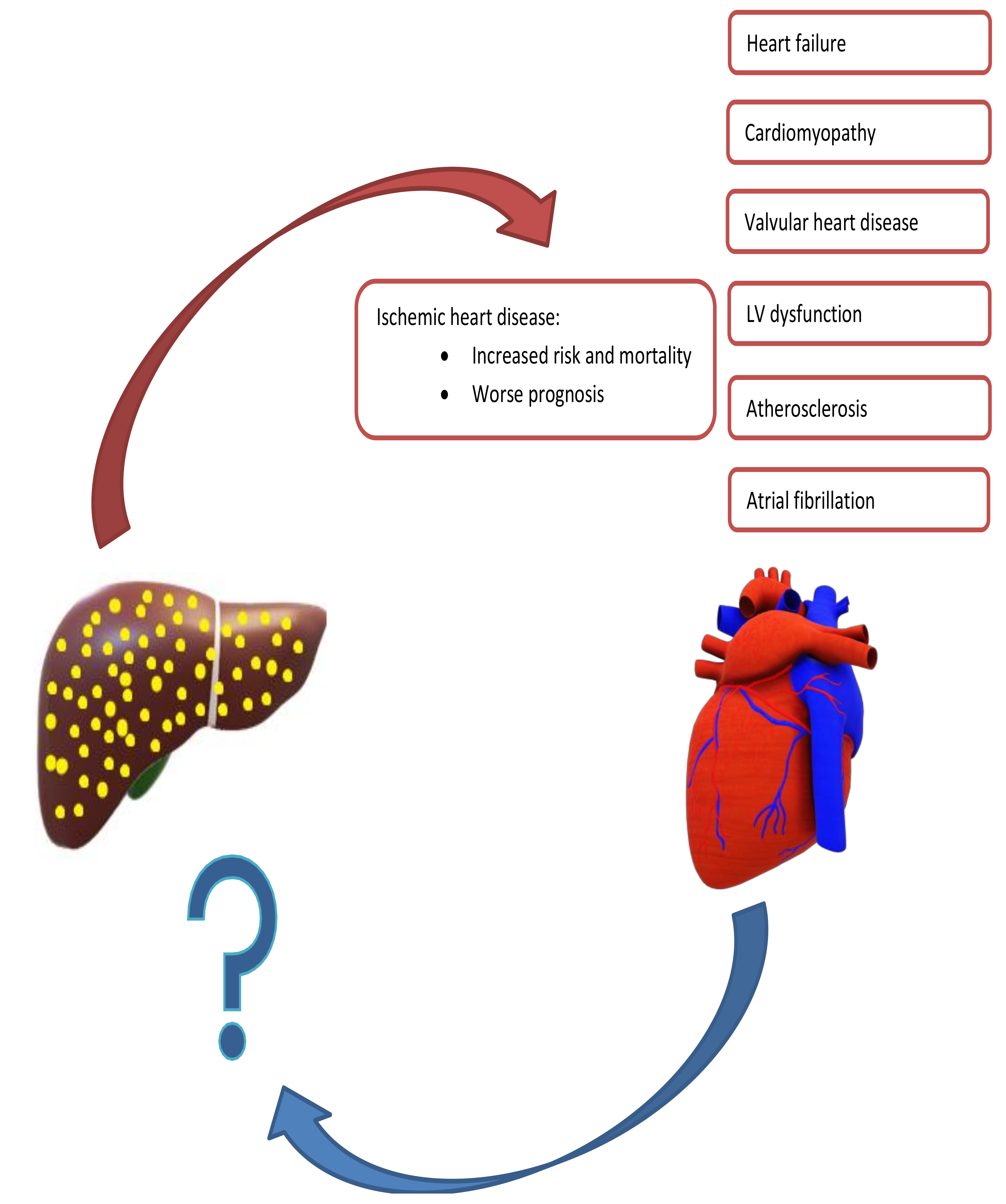
There is significant data suggesting that liver function actually is a risk factor for cardiac disease. Liver and Heart Although the liver and heart partner together to ensure blood circulates healthfully throughout the body few people consider the two to be a team. In their clinical practice physicians can face heart diseases chronic or acute heart failure affecting the liver and liver diseases affecting the heart.
We found that when we looked at coronary heart disease for example there is an abundance of disease in those who carry hazardous liver genes compared to. HF may lead to liver disease which adversely affects prognosis and complicates management of HF. In fact the liver receives up to 25 of cardiac output and is therefore highly sensitive to reduction in blood flow.
MONDAY June 24 HealthDay News -- A new study adds to growing evidence of a link between a common liver disease associated with obesity and high risk for heart disease. Systemic diseases can also affect both heart and liver. This is because systemic disorders and diseases affect both organs alcohol abuse drugs inflammation autoimmunity infections and because of complex cardiohepatic interactions.
Understanding the mutual relationship between the liver and the heart is important for both hepatologists and cardiologists. The largest organ inside your body your liver performs hundreds of vital functions.
The largest organ inside your body your liver performs hundreds of vital functions.
The largest organ inside your body your liver performs hundreds of vital functions. This is because systemic disorders and diseases affect both organs alcohol abuse drugs inflammation autoimmunity infections and because of complex cardiohepatic interactions. Therefore it is crucial in clinical practice to identify complex interactions between heart and liver in order to provide the best treatment for both. There is significant data suggesting that liver function actually is a risk factor for cardiac disease. The right and left sides of the heart act cooperatively in clinical and histologic liver disease related to CHF. Heart failure HF and liver disease often co-exist. MONDAY June 24 HealthDay News -- A new study adds to growing evidence of a link between a common liver disease associated with obesity and high risk for heart disease. Liver enzymes are special proteins found in liver cells. Thus it appears that hepatic congestion secondary to right-sided heart disease may prime the liver for ischemic insults from low cardiac output and reduced hepatic blood flow and oxygenation due to left-sided heart failure.
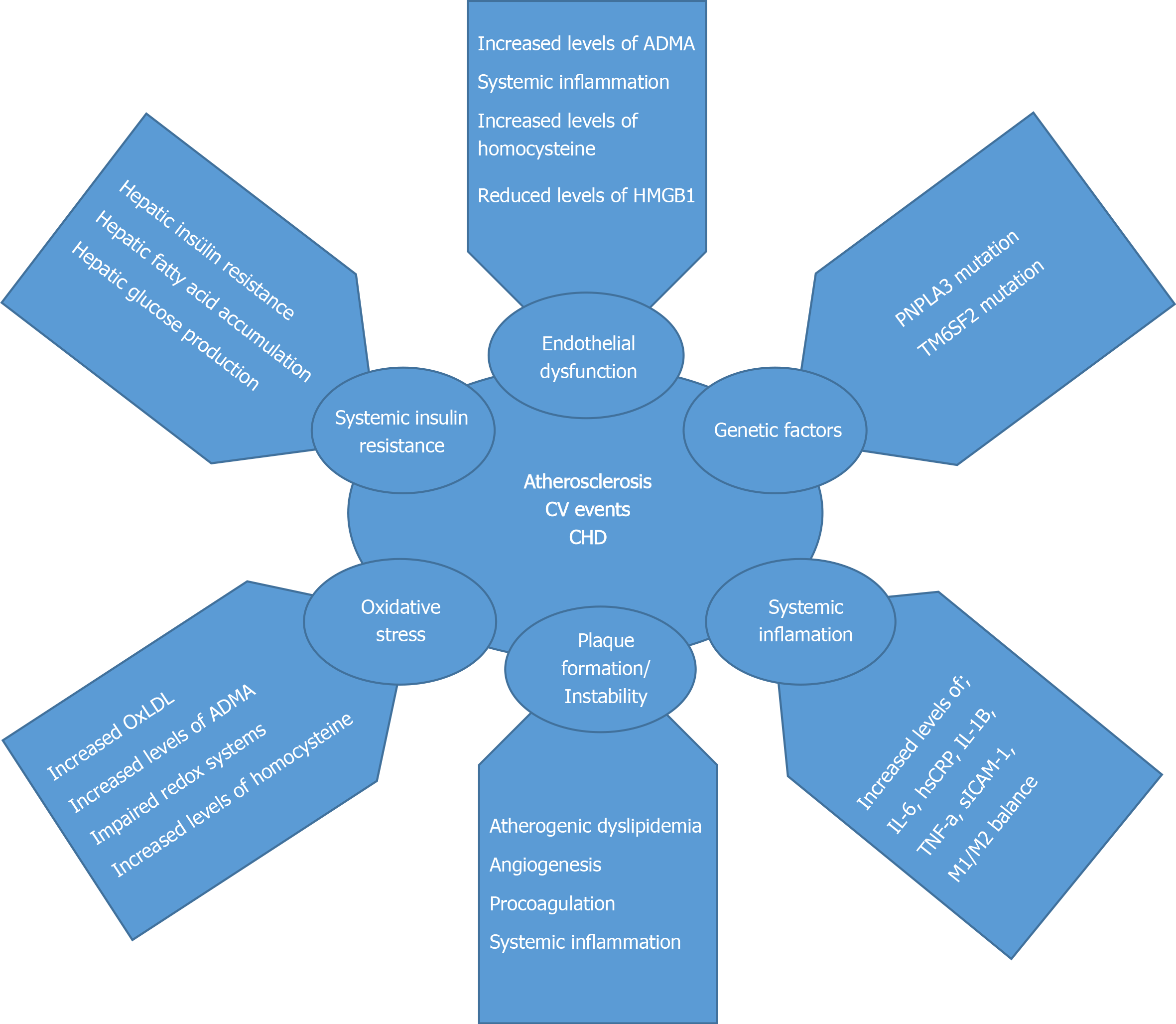
Thus it appears that hepatic congestion secondary to right-sided heart disease may prime the liver for ischemic insults from low cardiac output and reduced hepatic blood flow and oxygenation due to left-sided heart failure. However research on atherosclerosis confirms a tight connection between liver and heart pathology. The right and left sides of the heart act cooperatively in clinical and histologic liver disease related to CHF. Within the experimental period of 8 weeks the metabolic disorders in the liver were more pronounced than in the heart suggesting that CKD-related extrarenal organ dysfunctions occurred sequentially rather than simultaneously. It converts food into fuel processes cholesterol clears harmful toxins from the blood and makes proteins that help. Thus it appears that hepatic congestion secondary to right-sided heart disease may prime the liver for ischemic insults from low cardiac output and reduced hepatic blood flow and oxygenation due to left-sided heart failure. There is significant data suggesting that liver function actually is a risk factor for cardiac disease.










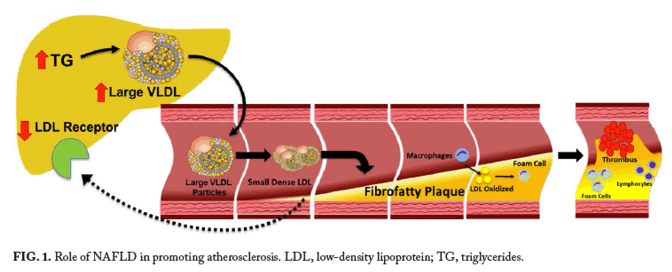







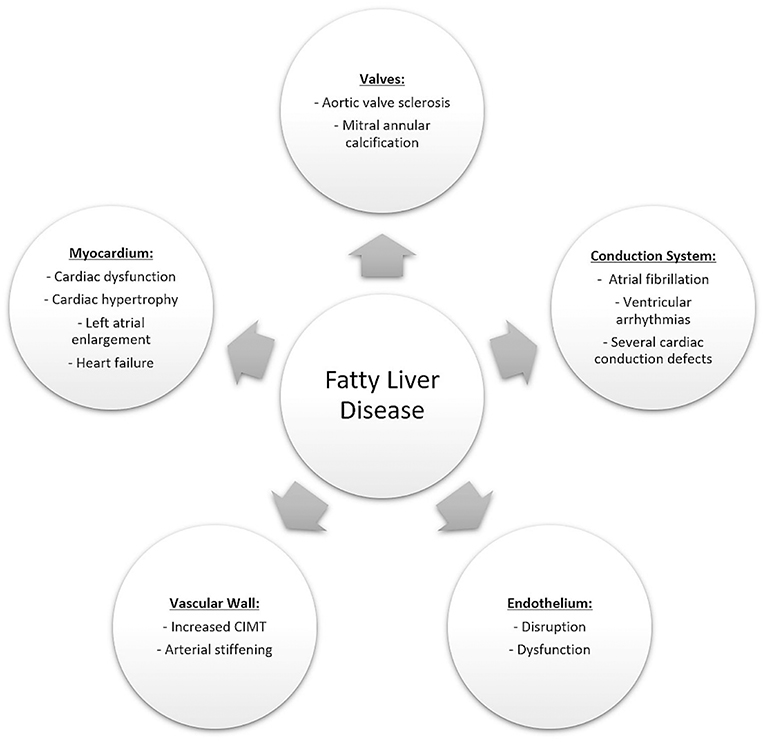
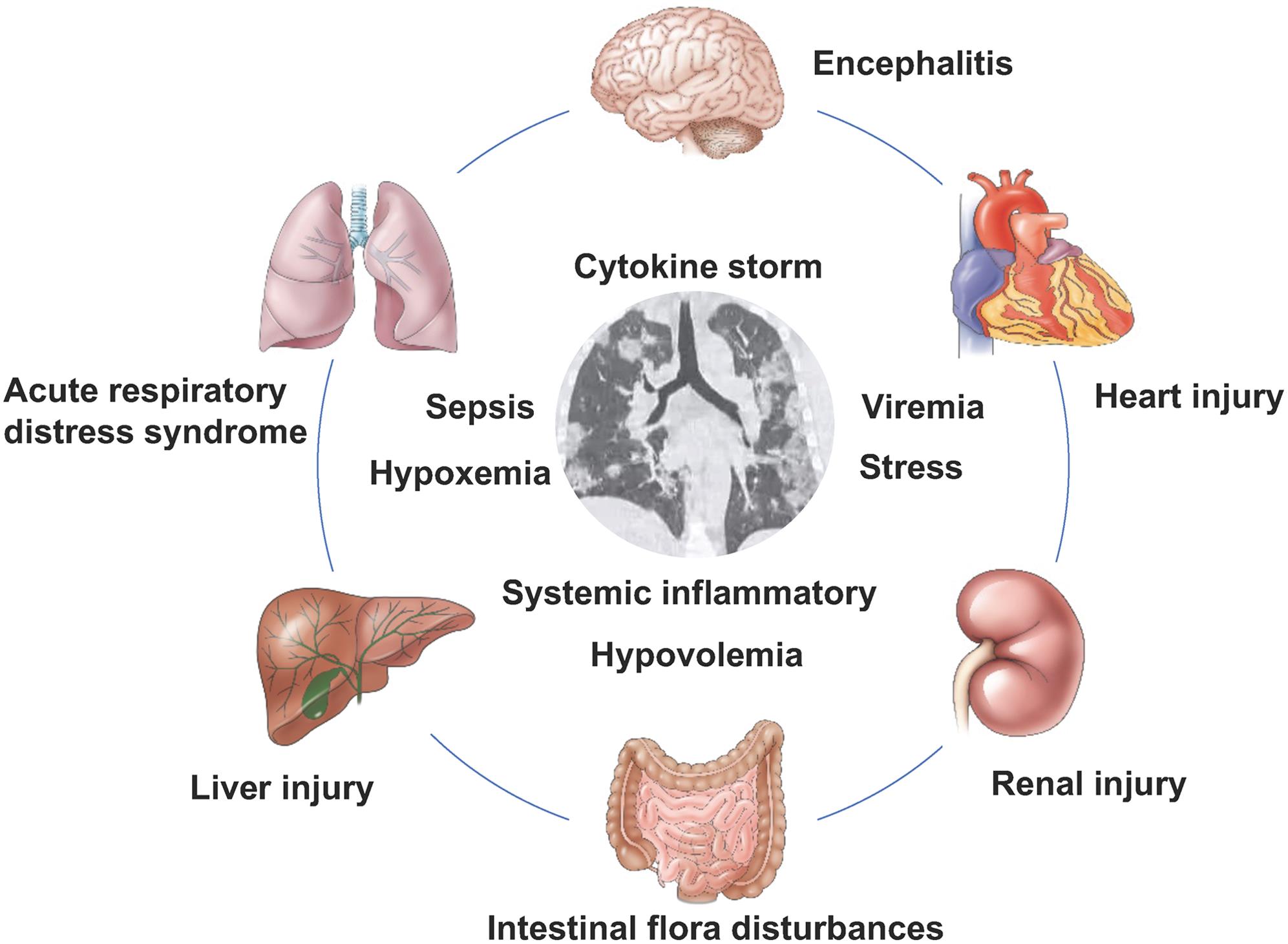









Posting Komentar untuk "Liver And Heart Disease"