Pathogenesis Of Celiac Disease
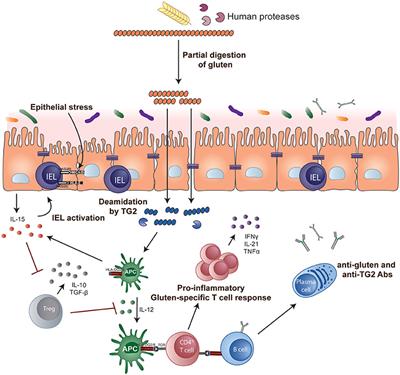
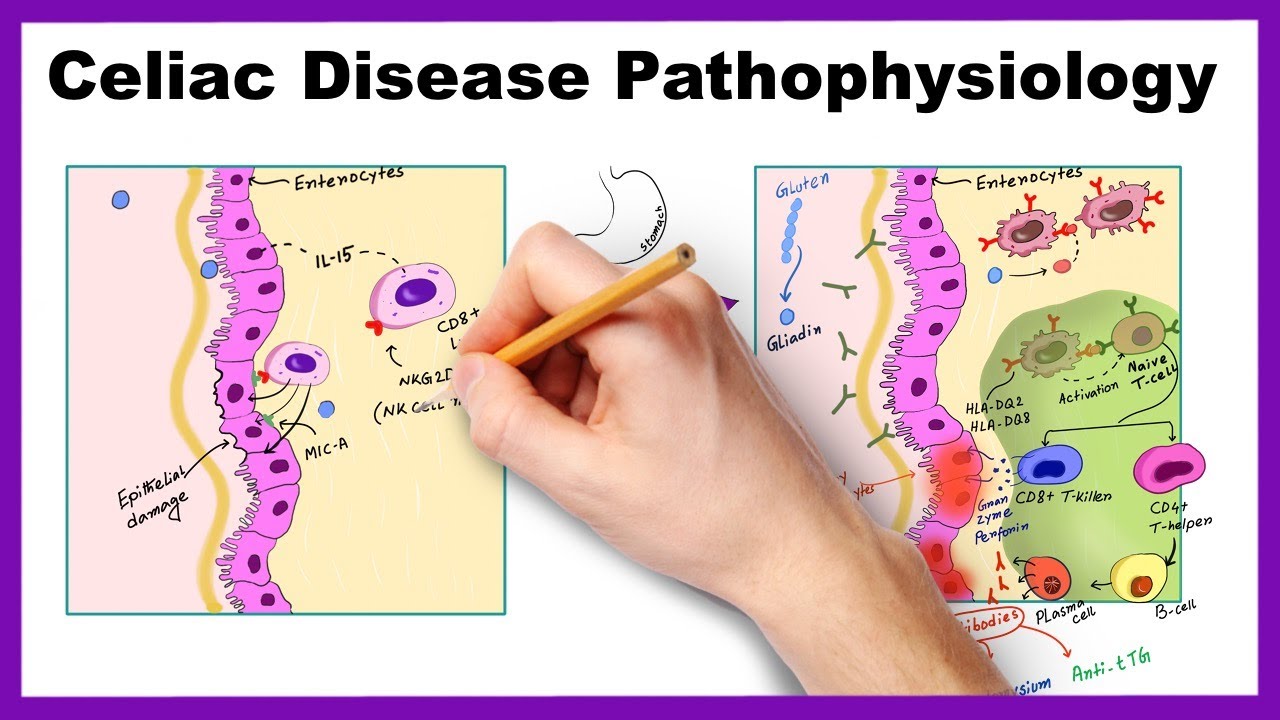
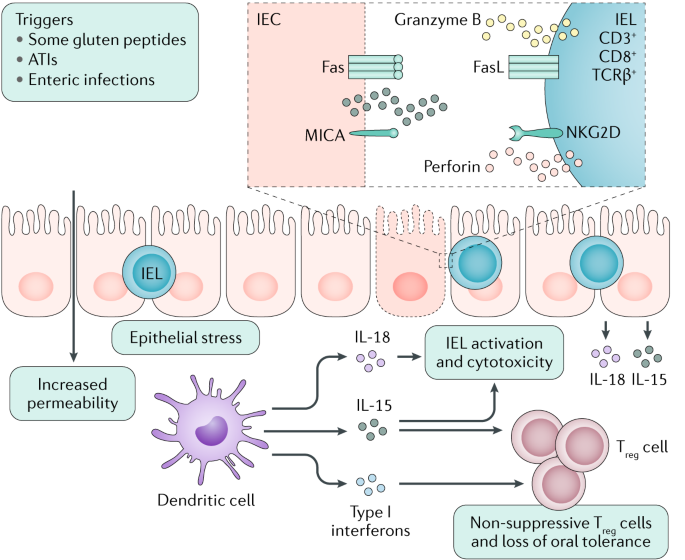
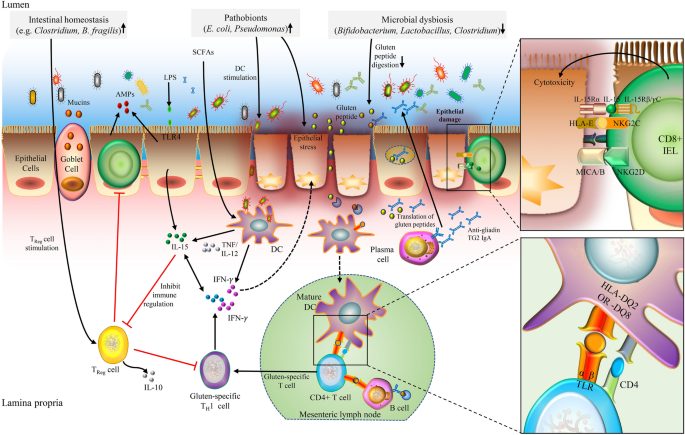
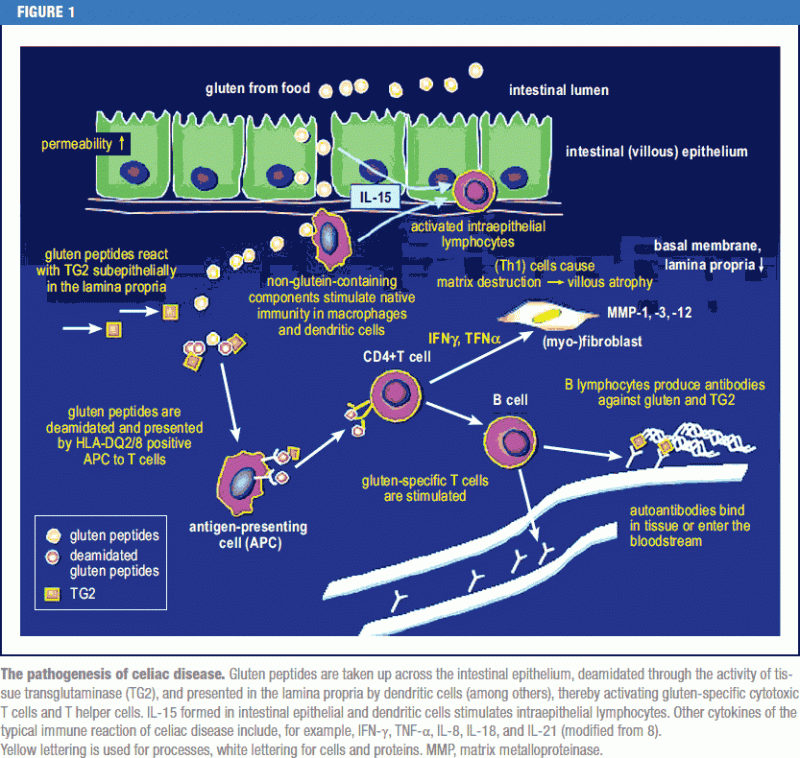
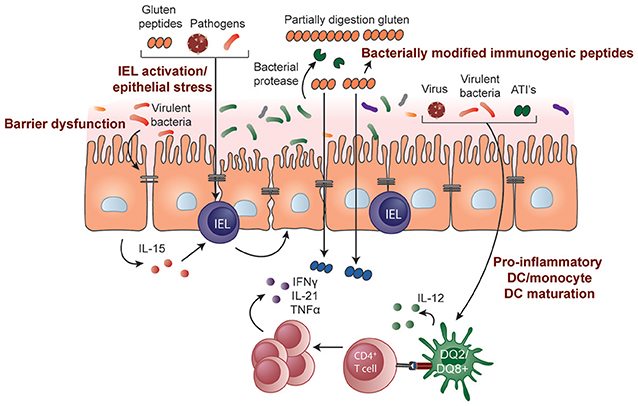
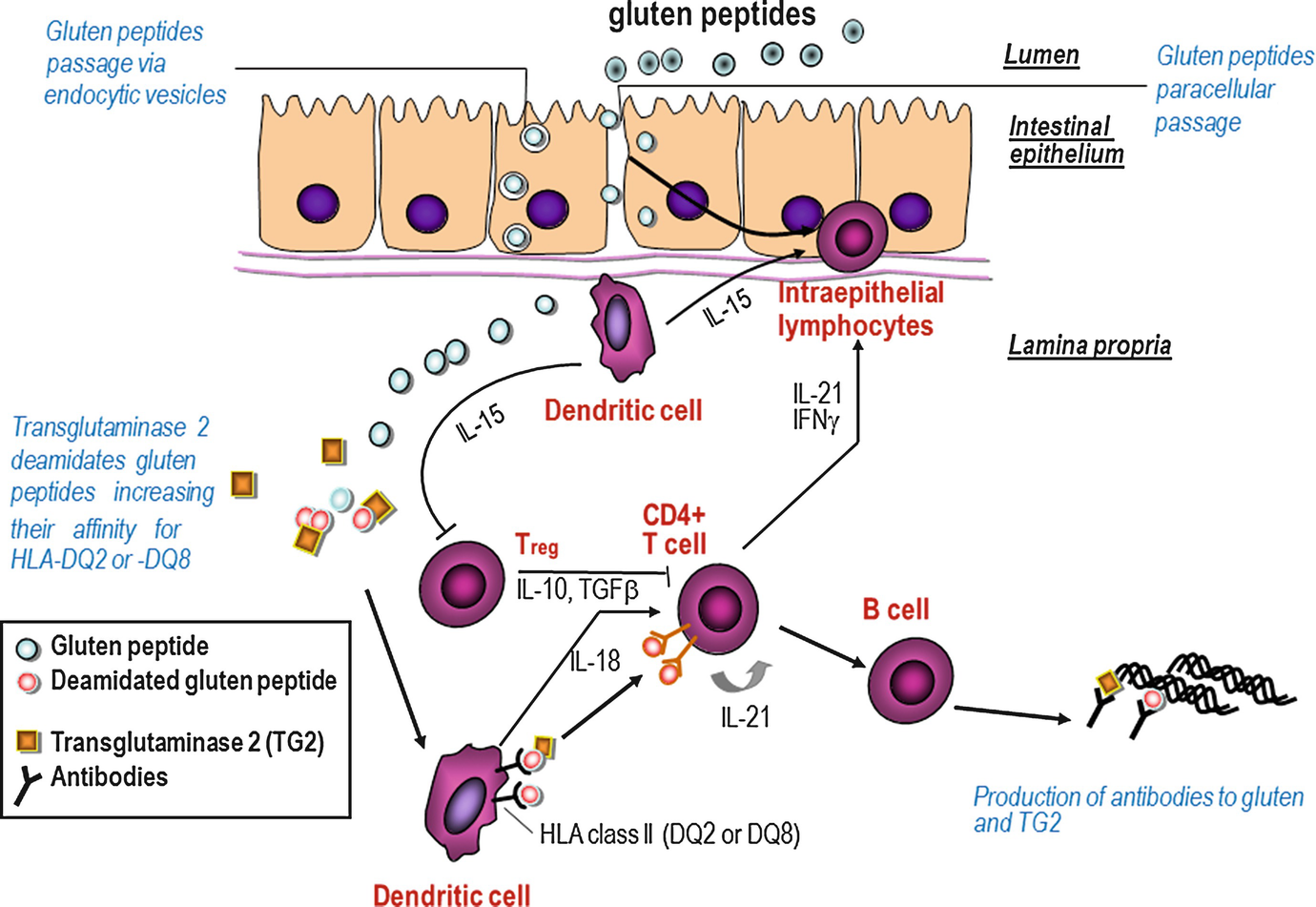
Pathogenesis of celiac disease. Disease pathogenesis involves interactions among environmental genetic and immunological factors. The role of adaptive immunity in celiac disease pathogenesis was first described in the 1970s when Ferguson and MacDonald 116117 reported an association of celiac disease with a lymphocyte-mediated immunity to gluten in the small intestine and that T cell-mediated immunity led to characteristic pathological changes such as villous atrophy in an allograft rejection model. Celiac disease CD is an autoimmune disorder with a systemic and chronic inflammatory immune response against gluten and gluten-related prolamins from wheat gliadin barley hordeins rye secalins and certain oat varieties avenins in genetically predisposed individuals 1 4.
Celiac disease also known as celiac sprue is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the small intestine produced by the ingestion of dietary gluten products in susceptible people. Genetic environment and immunologic With regard to genetics the CCA points out that more than 97 of celiac patients have the genetic markers HLA DQ2 andor HLA DQ8. Advances in the understanding of gluten related pathology and the evolution of gluten-free foods pp163-191 Edition.
Celiac disease occurs in any individual due to an interaction of genetic factors environmental factors and gluten. The environmental factors include gastrointestinal infections in childhood timing and amount gluten ingestion around the time of weaning and the presence. Whether the nearest cousin oats contributes to celiac disease remains controversial.
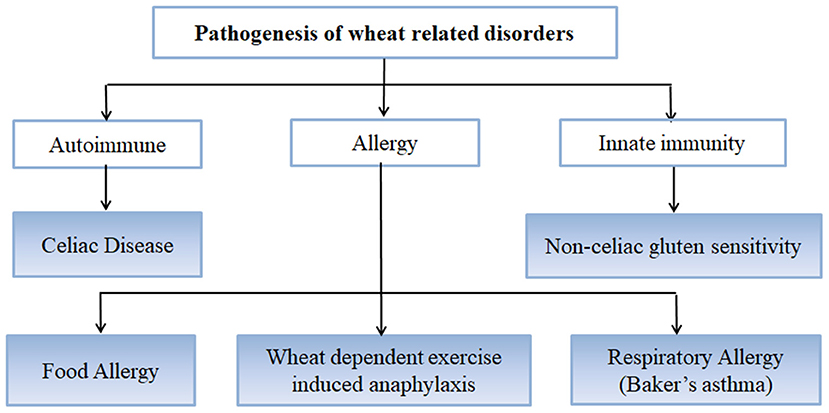
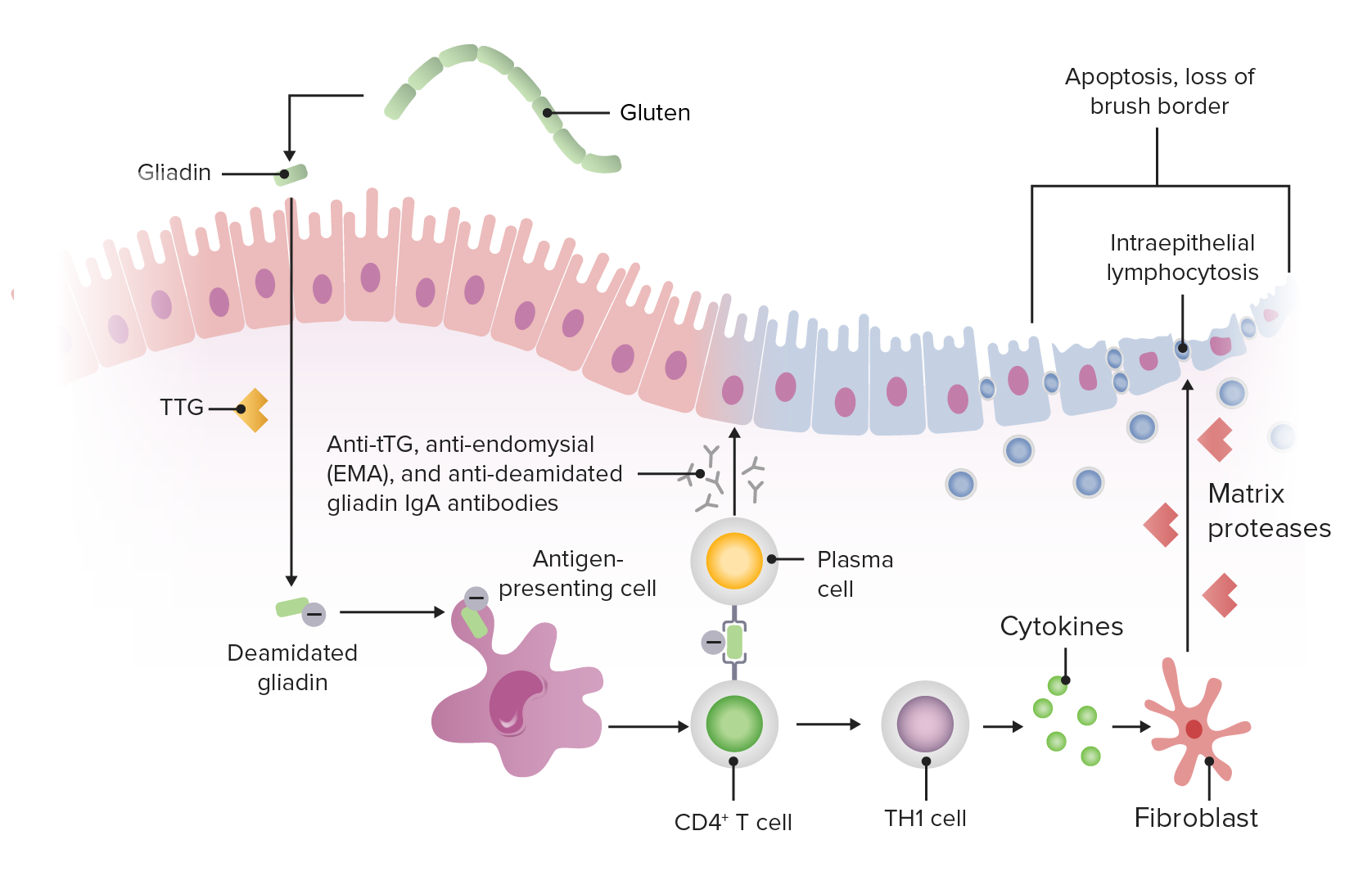
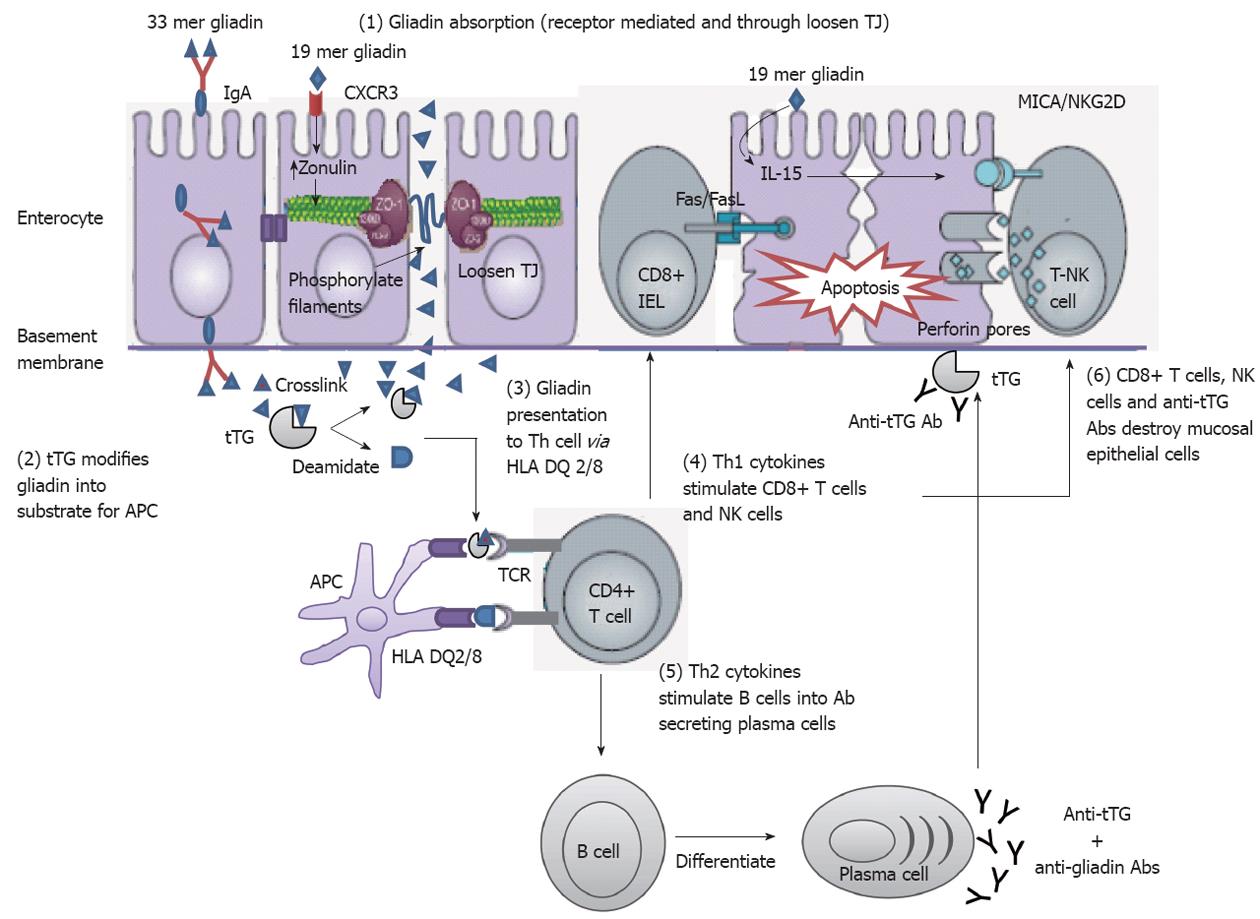
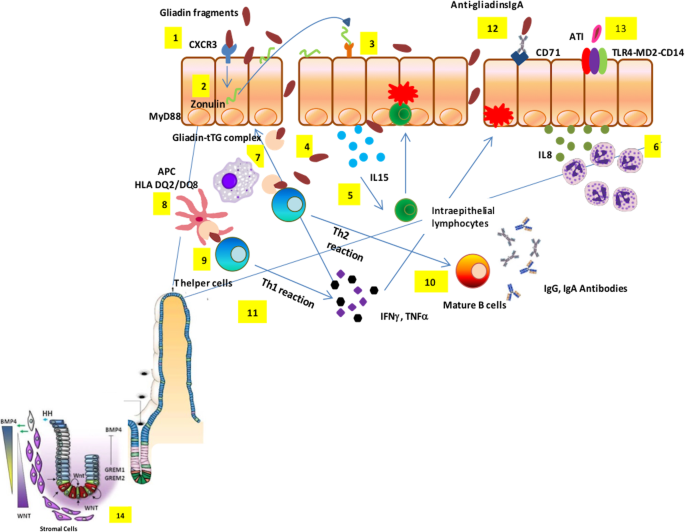
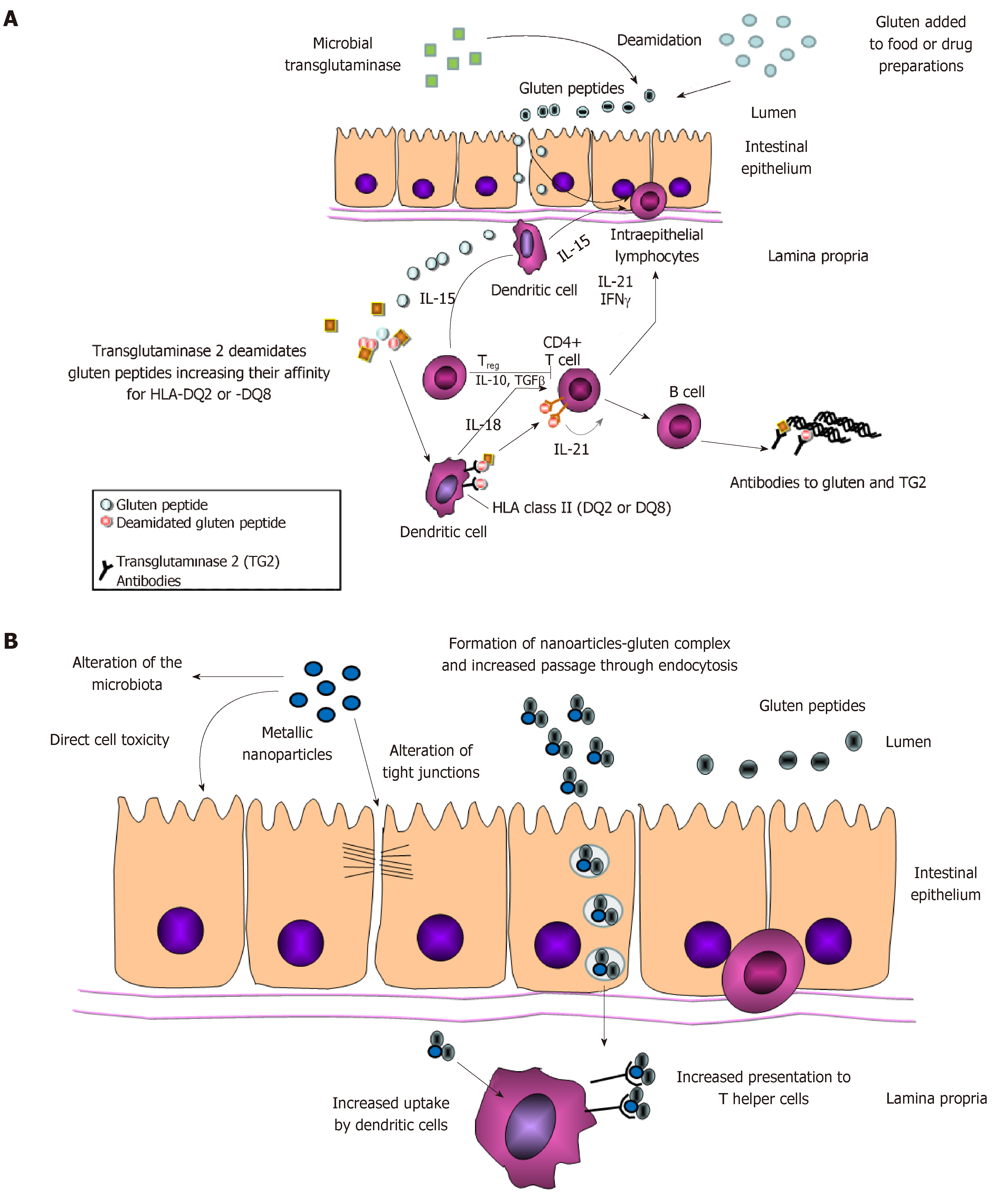
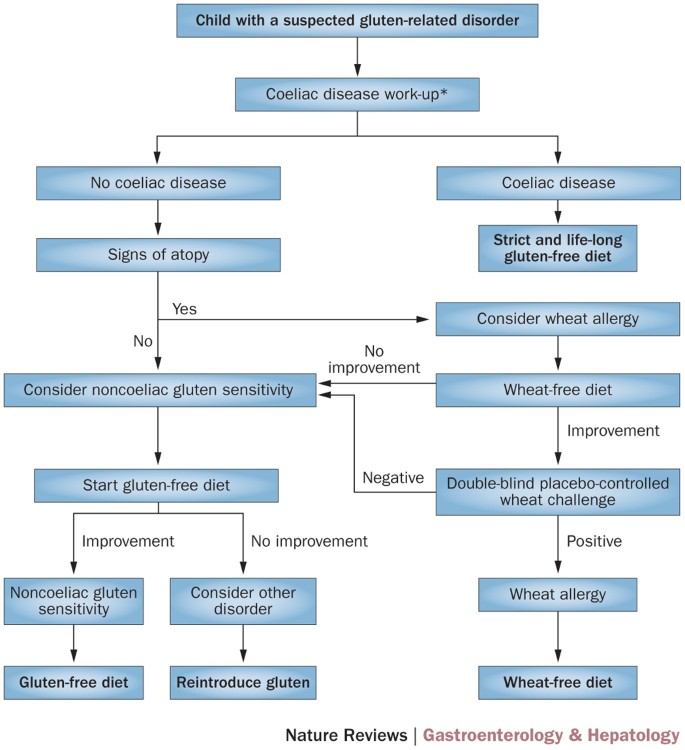
Another gluten related disorder is non-celiac gluten-sensitivity in which innate immune-response occurs in patients along with gastrointestinal and non-gastrointestinal symptoms that disappear upon removal of gluten from the diet. Autoantibodies against tTG are a very sensitive and specific marker for CD. Celiac disease has a complex pathology resulting from interaction between a number of genetic and exogenous factors.
Wheat is one of the most important cereals and with the. In addition to HLA genetic predisposition tTG autoantigens play a crucial role in CD pathogenesis. According to the Canadian Celiac Association CCA the pathogenesis of celiac disease consists of three factors.
The classification of cereals reveals an initial clue to the pathogenesis of celiac disease. At this point of time therapies for CD patients are non-existent. It is triggered by the gluten proteins of wheat barley and rye.
There have been a number of advances in our understanding of the pathogenesis of coeliac disease in particular the mechanisms whereby gluten epitopes are processed become modified by tissue. Celiac disease is characterized by small intestinal mucosal injury and nutrient malabsorption in genetically susceptible individuals following the dietary ingestion of gluten The pathogenesis of disease involves interactions between environmental genetic and immunologic factors.
Celiac disease occurs in any individual due to an interaction of genetic factors environmental factors and gluten.
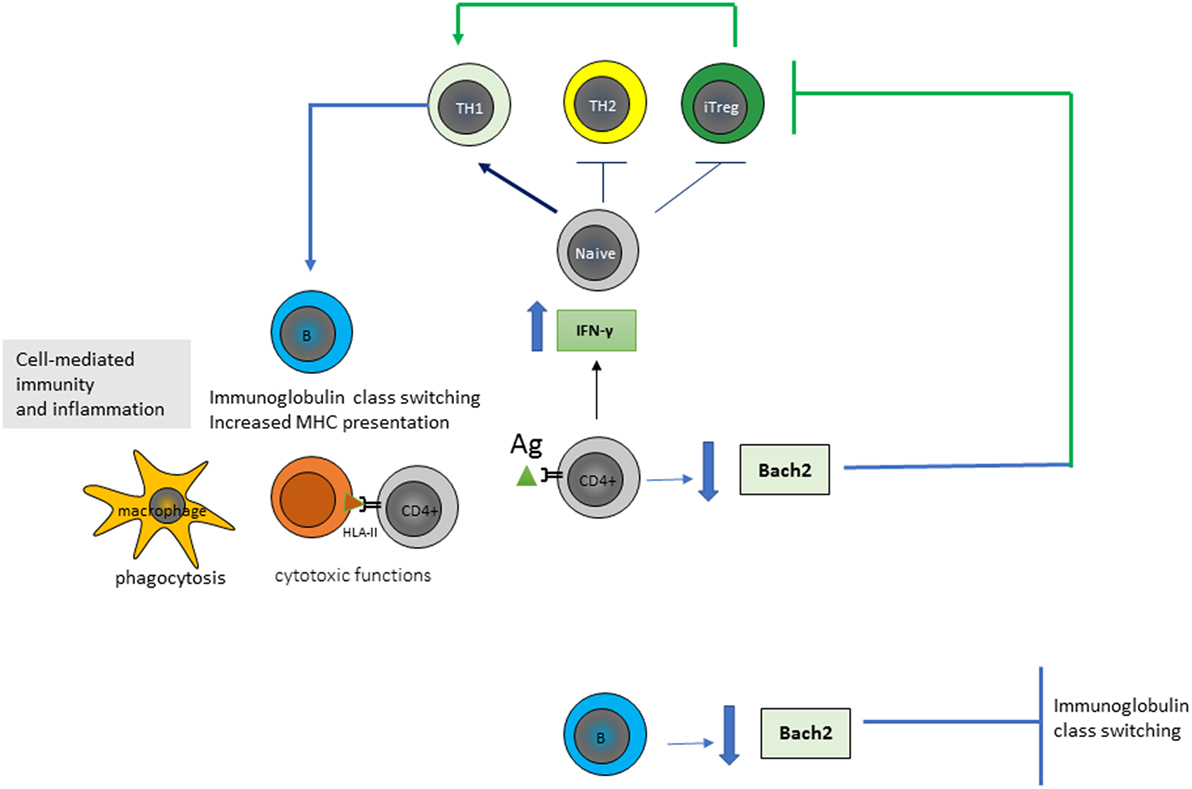
Wheat barley and rye are closely related cereals and they are all toxic to patients with celiac disease. Whether the nearest cousin oats contributes to celiac disease remains controversial. Celiac disease also known as celiac sprue is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the small intestine produced by the ingestion of dietary gluten products in susceptible people. Disease pathogenesis involves interactions among environmental genetic and immunological factors. Celiac disease is characterized by small-intestinal mucosal injury and nutrient malabsorption in genetically susceptible individuals in response to the dietary ingestion of wheat gluten and similar proteins in barley and rye. The classification of cereals reveals an initial clue to the pathogenesis of celiac disease. In addition to HLA genetic predisposition tTG autoantigens play a crucial role in CD pathogenesis. Pathogenesis of celiac disease Celiac disease results from activation of both a cell-mediated T-cell and humoral B-cell immune response. Another gluten related disorder is non-celiac gluten-sensitivity in which innate immune-response occurs in patients along with gastrointestinal and non-gastrointestinal symptoms that disappear upon removal of gluten from the diet.
All patients express the antigen-presenting molecules human leukocyte antigen-DQ2 HLA-DQ2 ando. The classification of cereals reveals an initial clue to the pathogenesis of celiac disease. Pathogenesis of Celiac Disease and Other Gluten Related Disorders in Wheat and Strategies for Mitigating Them Gluten Free Diet GFD. Celiac disease is characterized by small-intestinal mucosal injury and nutrient malabsorption in genetically susceptible individuals in response to the dietary ingestion of wheat gluten and similar proteins in barley and rye. Advances in the understanding of gluten related pathology and the evolution of gluten-free foods pp163-191 Edition. At this point of time therapies for CD patients are non-existent. Whether the nearest cousin oats contributes to celiac disease remains controversial.
































Posting Komentar untuk "Pathogenesis Of Celiac Disease"