Von Willebrand Disease And Anesthesia
Von willebrand disease and anesthesia. This article examines the anesthetic management of a parturient with a known diagnosis of von Willebrand disease. Neuraxial anesthesia was used for the patient. Von Willebrands disease is caused by deficiencies in von Willebrands factor which plays a crucial role in the adhesion of platelets to the sub-endothelium during vascular injury and is essential for normal primary haemostasis to occur.
Unlikely to be effective. It is also important to gauge your approach based on the surgery being performed the likelihood of high blood loss. High risk for perioperative bleeding.
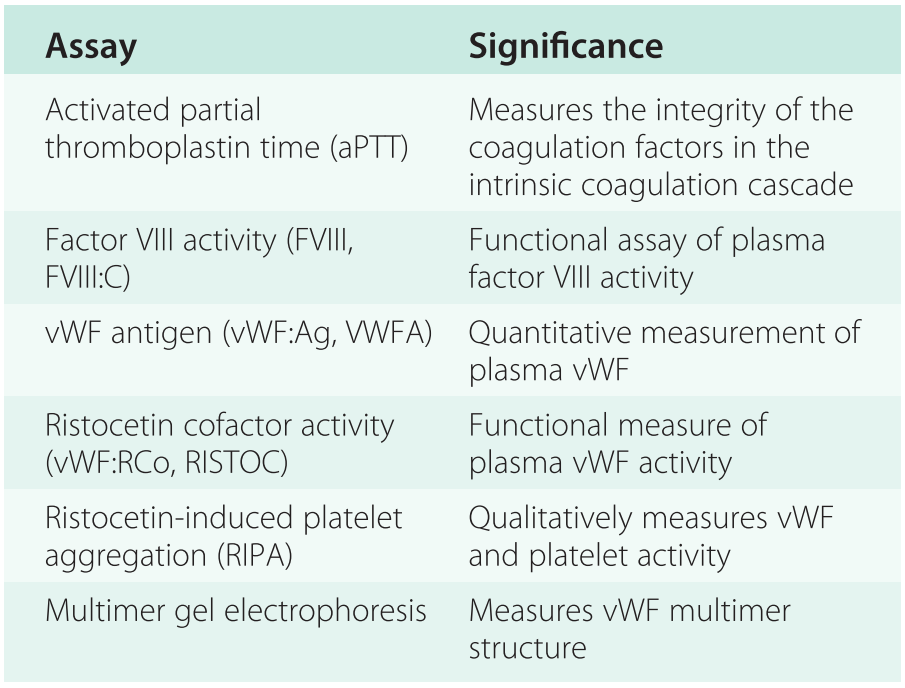
Von Willebrand factor antigen vWFAg 28 and Ricof level 42. Von Willebrands disease is a hereditary deficiency of von Willebrands factor VWF causing platelet dysfunction. Von Willebrands disease represents the most common of the inherited bleeding disorders with a prevalence as great as 1 of the population.
Von Willebrand disease VWD is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. 2 There are three subtypes of von Willebrands disease. Fearing the devastating neurological complications in a parturient with the von Willebrand disease secondary to paucity of studies defining the guidelines to assess the risk of bleeding complications anesthesiologists are often reluctant to administer neuroaxial anesthesia.
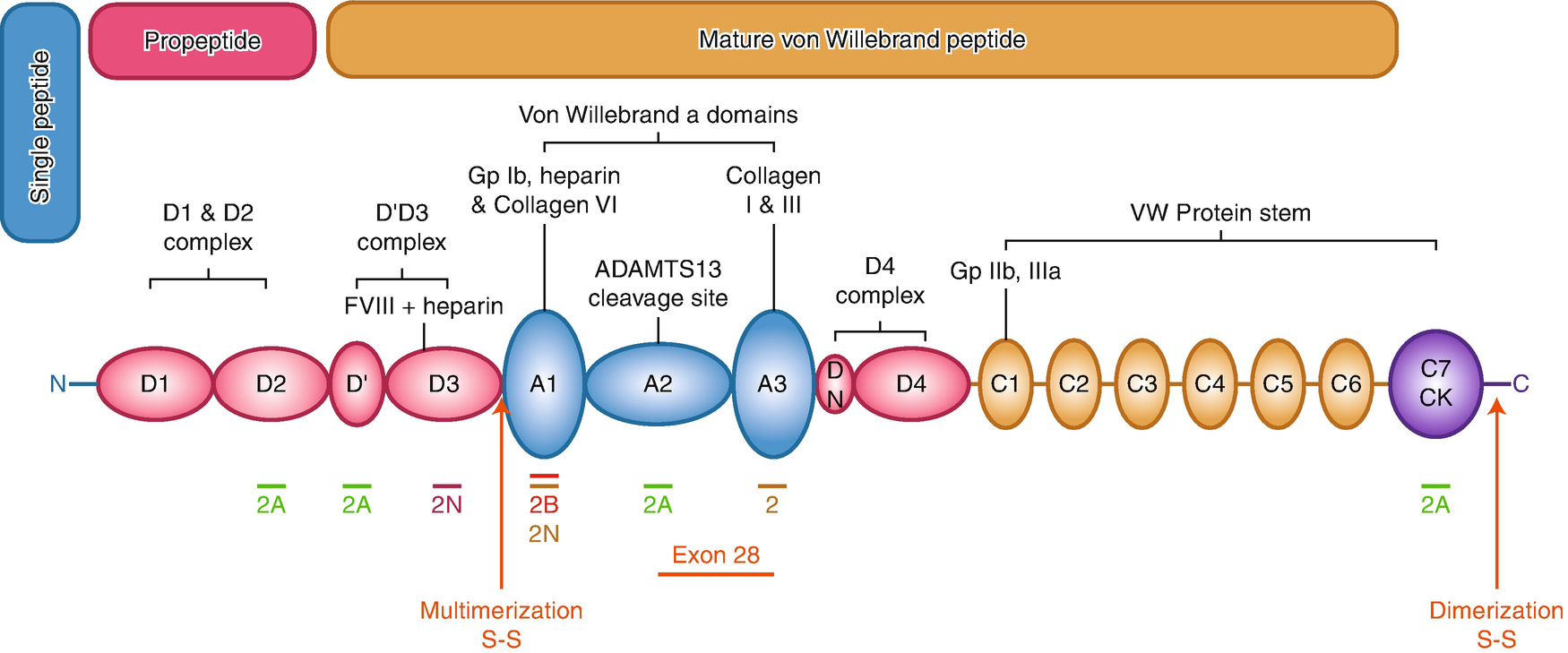
Her laboratory results were as follows. Von Willebrands factor circulates in a non-covalent complex with factor VIII. First described by Erik Adolf von Willebrand in 1926 VWD is a congenital bleeding disorder characterized by a lifelong tendency toward easy bruising frequent epistaxis.
Von Willebrands disease is the most common hereditary coagulopathy but it is underdiagnosed due to the complexity of the disease itself. Sequelae of bleeding in enclosed spaces joints intracranial pericardium thorax Potential contraindication to neuraxial anesthesia analgesia. Epidural anesthesia combined with general anesthesia was performed in a patient with type 1 von Willebrand disease VWD.
Consultation with hematology for factor optimization replacementsupplementation Goals. The disease was first described by Erik von Willebrand more than 70 yr ago.
Subtypes of this disease are characterized by quantitative andor qualitative abnormalities of von Willebrand factor a plasma protein essential to platelet adhesion and the stabilization of factor VIII.
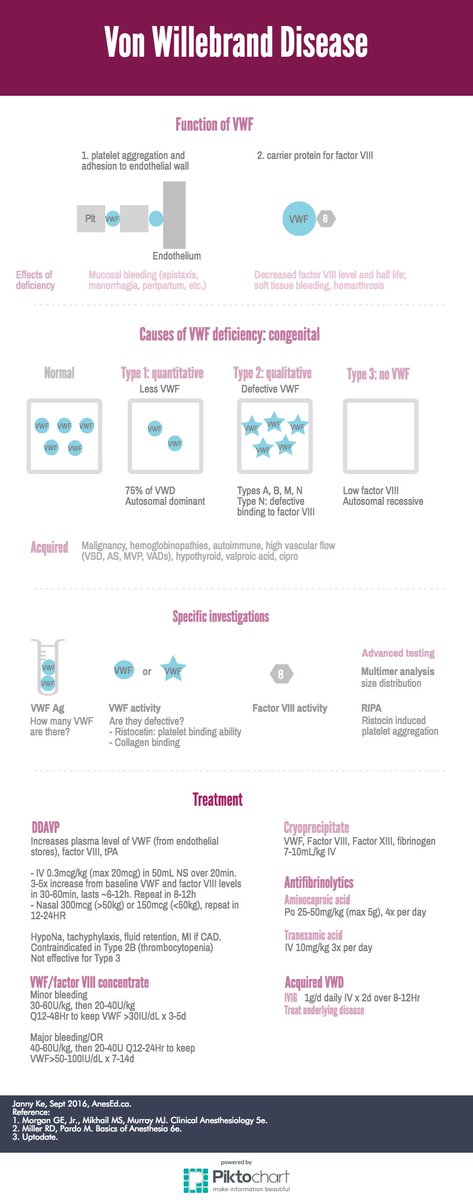
Trial of dDAVP if not responding use vWF concentrate or cryprecipitate if emergency. Von Willebrands disease is an autosomal dominant disease with several subtypes and mild and severe forms. An autosomally inherited congenital bleeding disorder von Willebrand disease involves a qualitative or quantitative deficiency of von Willebrand factor vWF a protein critical for proper platelet adhesion and protection against coagulant factor degradation. Von Willebrand disease VWD is a family of bleeding disorders caused by an abnormality of the von Willebrand factor VWF. It is also important to gauge your approach based on the surgery being performed the likelihood of high blood loss. Trial of dDAVP if not responding use vWF concentrate or cryprecipitate if emergency. An evidenced-based approach is prudent when this derangement is coupled with a potentially fatal obstetric complication. Dominant and recessive patterns of inheritance exist. Von Willebrands disease represents the most common of the inherited bleeding disorders with a prevalence as great as 1 of the population.
Von Willebrands disease is caused by deficiencies in von Willebrands factor which plays a crucial role in the adhesion of platelets to the sub-endothelium during vascular injury and is essential for normal primary haemostasis to occur. Von Willebrands disease is a hereditary deficiency of von Willebrands factor VWF causing platelet dysfunction. An autosomally inherited congenital bleeding disorder von Willebrand disease involves a qualitative or quantitative deficiency of von Willebrand factor vWF a protein critical for proper platelet adhesion and protection against coagulant factor degradation. Bleeding tendency is usually mild. Subtypes of this disease are characterized by quantitative andor qualitative abnormalities of von Willebrand factor a plasma protein essential to platelet adhesion and the stabilization of factor VIII. 11 Major symptoms include mucocutaneous bleeding including epistaxis easy bruising and heavy menstrual bleeding as well as provoked bleeding in the setting of surgery and. Neuraxial anesthesia was used for the patient.



































Posting Komentar untuk "Von Willebrand Disease And Anesthesia"